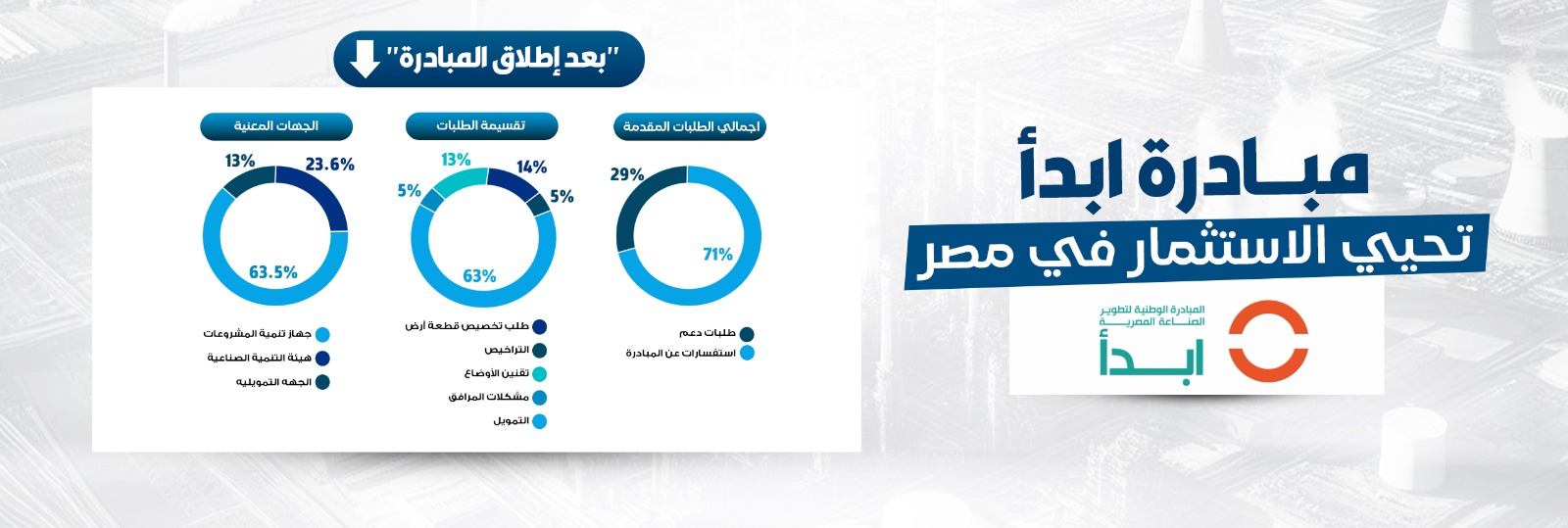
التقنية للأستشارات الأقتصادية
شركة التقنية للاستشارات الإقتصادية، دراسة الجدوى وتنفيذ المشروعات، شركة معتمدة رائدة في الاستشارات الإستثمارية والإدارية للشركات والمؤسسات المحلية والدولية، سابقة أعمال كبيرة من المشاريع ودراسات الجدوى الناجحة في مصر والوطن العربي وأوروبا، نأخذ بيدك لطريق النجاح